Monocyte migration across the human
blood-brain barrier
The potential contribution of circulating monocytes/macrophages to the
inflammatory process of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is studied in a physiological
model proposed by Fiala et al. [1].
Under normal circumstances, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) filters out
the circulating monocytes from the brain tissue. However, chemotactic stimulus
of inflammatory regions of the brain may attract such monocytes which then
permeate the BBB. A large number of Aß deposits are present
in the AD brain together with the presence of multiple inflammatory molecules.
These are thought to induce the monocytes transmigration of the BBB, and
movement into the vicinity of Aß deposits.
Differentiation of monocytes into macrophages:
-
Human blood monocytes were obtained from peripheral blood of healthy donors.
-
1×106 monocytes were incubated in 1 ml of RPMI medium
during 8 days (alone or with different concentrations of Aß1-42).
-
400ml of RPMI and 20ml
of MTT solution were added to each well, and incubated at 37 oC
for 4 hrs.
Cultures of peripheral monocytes:
-
1×106 monocytes were cultured in 24-well plates using
1 ml of RPMI medium and various concentration of Aß1-42 for
48 hrs.
Elisa essays of cytokines and chemokines:
-
TNF-a, IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12 levels in the culture
media were obtained by a ßandwich" ELISA.
-
IL-1b and MCP-1 (human monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1) levels were obtained by using Quantikine ELISA.
Transmigration of monocytes:
-
160 mg of Aß1-42 in 35 ml
of medium were placed in 6 wells, and 2×104 monocytes
in 1 ml of DME-S medium were added. After 16 hrs of incubation, 5×105
monocytes in DME-S medium were added for an incubation time of 24 hrs.
Results:
Aß induces secretion of cytokines by cultured monocytes:
-
5×105 monocytes were cultured in the presence of increasing
concentrations of Aß to induce cytokine secretion. In figure
2 of Fiala's et al. we can observe different secretion levels for
increasing concentrations of Aß. Concentrations were compared
to that of the ones stimulated by the control media containing DMSO. The
data obtained for the different Aß concentration levels:
| A-b(mg/ml) |
TNF-a(pg/ml) |
IL-6(pg/ml) |
IL-12(pg/ml) |
IL-1b(pg/ml) |
| 0.25 |
500 |
20 |
1 |
|
| 2.5 |
800 |
110 |
7 |
|
| 25 |
1400 |
140 |
10.5 |
25 |
Moreover, we have that 8 mg/ml of IL-1b
were secreted with 8.1 pg/ml of Aß1-42.
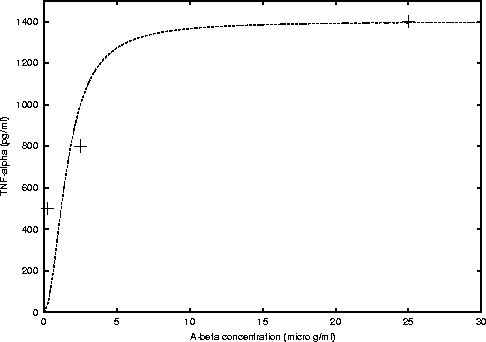
Some Michaelis-Menten type functions are eye-fitted to the above data.
If c is the cytokine concentration in pg/ml, and x is the Aß
concentration. We have that for TNF-a secretion
the function is
where, cmax = 1400 and K = 2.5 (see figure 1).
|
Figure 1: Michaelis-Menten curve fitted to the data
obtained from figure 2 A) of Fiala's et al. paper [1].
|
|
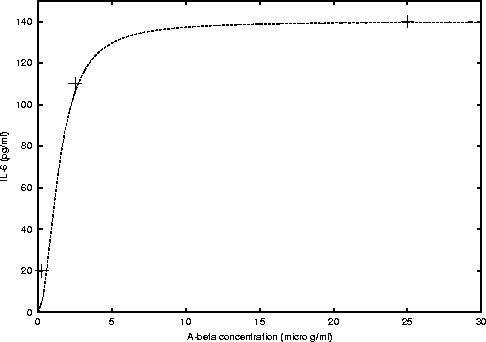
For IL-6 we found
where, cmax = 140 and K = 2 (see figure 2).
|
Figure 2: Michaelis-Menten curve fitted to the data
obtained from figure 2 B) of Fiala's et al. paper [1].
|
|
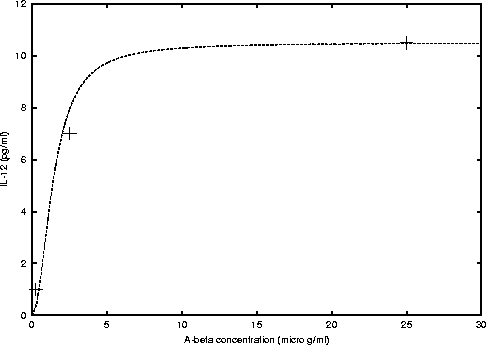
And for IL-12 we have
where, cmax = 10.5 and K = 2 (see figure 3).
|
Figure 3: Michaelis-Menten curve fitted to the data
obtained from figure 2 C) of Fiala's et al. paper [1].
|
|
There were some individual donor fluctuations in the amount of cytokine
secretion when monocytes were stimulated with Aß1-42. Eight
individual donors were investigated whose monocytes were treated with 2.5
µM of Aß1-42. In table 1 of Fiala's et al.,
we can compare the results. Again, concentrations were compared to those
stimulated by the control media containing DMSO.
Aß1-42 with monocytes stimulate monocyte transmigrating
across the BBB model:
The model consisted of placing a monolayer of human endothelial cells
derived from cerebral microvessels and human astrocytes separating the
vascular side (upper chamber) from the brain parenchymal side (lower chamber).
In a control experiment, 5×105 human monocytes were placed.
Figure 4 of Fiala's et al. paper shows that:
-
For only medium concentration, after 24 hrs of incubation time, around
700 monocytes migrated to the lower chamber ( ~ 1%).
-
When 2×104 monocytes were introduced into the lower chamber
prior to the experiment, migration of monocytes from the upper to the lower
chamber increased to approximately 3000 ( ~ 2%).
-
Addition of 10 ml, 25 µM of Aß1-42
at the bottom of the lower chamber followed by medium resulted in the transmigration
of 2×104 monocytes in 24 hrs ( ~ 10%).
-
When the lower chamber contained both, Aß1-42 and 2×104
monocytes transmigration increased to 6.3×104(
~ 26%).
Conclusions :
It has been strongly suggested that inflammation plays a pivotal role
in the pathogenesis of AD and development of dementia. In vitro cultures
of human microglia obtained from rapid autopsies from individuals with
AD secreted 100-fold or more IL-1b, IL-6 and
TNF-a than those cells from nondemented subjects.
In this study fluctuations in cytokine secretion elicited by Aß
in different donors are thought to be due to the individual's immunological
responsiveness. Also, in this study the authors show the proinflammatory
effects of Aß1-42 on peripheral monocytes. It is suggested
that some of the microglia-like cells surrounding the Aß fibrils
are transmigrated monocytes from the BBB. In a dose and time-dependent
manner, it was shown how Aß induced differentiation of monocytes
into macrophages, as well as some monocyte migration across the BBB.
Reference:
[1] Fiala M, Zhang L, Gan X, Sherry B, Taub D, Graves MC, Hama, S, Way D, Weinand M, Witte M, Lorton D, Kuo Y_M, Roher AE (1998). Amyloid-beta induces chemokine secretion and monocyte migration across human blood-brain barrier
model. Molec Med 4: 480-489.Abstract
File translated from TEX by TTH,
version 2.60.
On 27 Jan 2000, 01:32.