Chromatic Aberration
![]()
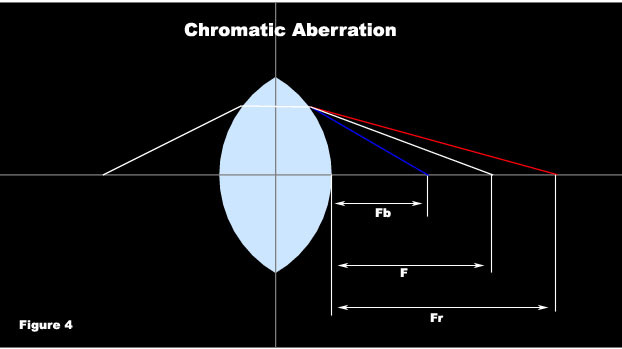
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum and v is the speed of light of the medium. Generally as the wavelength increases, index decreases since the index of refraction for blue light (shorter wavelengths) is larger than that of red light (longer wavelengths) as seen in Figure 4. So when light hits a lens, the different colors will leave at different speeds therefore each will have different focal lengths, and hence light disperses. Furthermore v is measured by a standard form known as Abbe's number:
![]()
nD is yellow sodium D lines (589.3nm), nF is the blue F line of hydrogen (486.1nm) and the red hydrogen C line (656.3nm). To see an example of it please go here.