Function: surfarrows - plot a 3D surface (parametric or cartesian) with arrows from a vector field at points on the surface.
Calling sequence:
surfarrows(fld,surf,s=a1..b1,t=a2..b2);
Parameters:
fld
- the vector field, either a 3-component list or vector expression in the parameters
s
and
t
(specifying the vectors in terms of those parameters) or a function of three variables whose values are 3-component lists or vectors (specifying the vector field in terms of the spatial coordinates
![]() ,
,
![]() and
and
![]() ).
).
surf
- the surface, either a 3-component list or vector expression in the parameters
s
and
t
(for a parametric representation of the surface) or a scalar expression in
s
and
t
(representing the
![]() coordinate while
s
and
t
are the
coordinate while
s
and
t
are the
![]() and
and
![]() coordinates respectively).
coordinates respectively).
s , t - names for the parameters.
a1 , b1 , a2 , b2 - endpoints for the parameter intervals. a1 and b1 must be constants, while a2 and b2 may depend on the first parameter s .
Optional arguments:
arrowgrid= [
![]() ,
,
![]() ]
for arrows in an
]
for arrows in an
![]() by
by
![]() grid, equally spaced in terms of the parameters of the surface (default is
arrowgrid=[8,8]
).
grid, equally spaced in terms of the parameters of the surface (default is
arrowgrid=[8,8]
).
scalefactor=
![]() to multiply arrow lengths by real constant
to multiply arrow lengths by real constant
![]() .
.
arrowthickness=
![]() for thickness of the arrow shaft (
for thickness of the arrow shaft (
![]() should be 0, 1, 2 or 3, default is the same as the
thickness
option if specified, or 3 if not).
should be 0, 1, 2 or 3, default is the same as the
thickness
option if specified, or 3 if not).
arrowcolour=
![]() to specify arrow colour (default is the same as the
colour
option if specified, or red if not). The alternate spelling
arrowcolor
is allowed.
to specify arrow colour (default is the same as the
colour
option if specified, or red if not). The alternate spelling
arrowcolor
is allowed.
other 3D surface plotting options.
Description:
This function creates a 3D plot data object which consists of a surface, plotted as with the command
plot3d(surf, s=a1..b1, t=a2..b2)
(including all options of the
surfarrows
command except
arrowgrid
,
scalefactor
,
arrowthickness
and
arrowcolour
), plus arrows representing the vector field
fld
drawn at points on the surface.
Unless the option scaling=constrained ("Projection, Constrained" on the plot menu or "1-1" on the context bar) is used, the shapes of the arrowheads may be distorted.
This function is part of the package surfarro in the Maple Advisor Database library, and must be loaded before use by the command with(surfarro); or with(surfarro,surfarrows); .
Examples:
> with(surfarro,surfarrows):
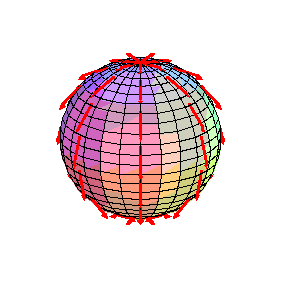
Surface is a sphere represented parametrically, vectors are tangent to meridians.
>
surf1:= [sin(t)*cos(s),sin(t)*sin(s),cos(t)];
F1:= diff(surf1,t);
surfarrows(F1, surf1, s = 0 .. 2*Pi, t = 0 .. Pi,
scalefactor=0.4, style=patch, scaling=constrained, orientation=[0,70]);
surf1 := [sin(t) cos(s), sin(t) sin(s), cos(t)]
F1 := [cos(t) cos(s), cos(t) sin(s), -sin(t)]
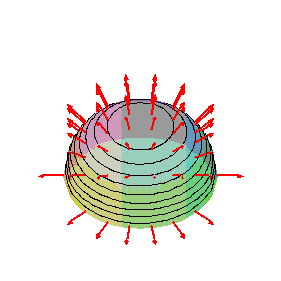
Surface is a hemisphere represented in Cartesian coordinates, vectors are normal to surface. Note that the
![]() interval depends on
interval depends on
![]() .
.
>
surf2:= sqrt(1-x^2-y^2);
F2:= [x,y,surf2];
surfarrows(F2,surf2, x = -1 .. 1, y = -0.999*sqrt(1-x^2) .. 0.999*sqrt(1-x^2), orientation = [90, 45],
scalefactor=1/3, style=patchcontour, scaling=constrained, arrowthickness = 2);
2 2
surf2 := sqrt(1 - x - y )
2 2
F2 := [x, y, sqrt(1 - x - y )]
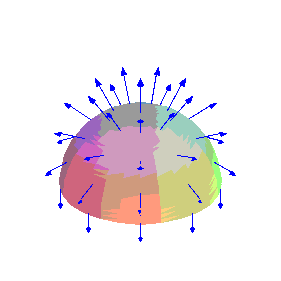
Parametric hemisphere, vector field is a function of
![]() ,
,
![]() and
and
![]() coordinates (a dipole field in this case):
coordinates (a dipole field in this case):
>
F3:= (x,y,z) -> [3*x*z, 3*y*z, 2*z^2-x^2-y^2];
surfarrows(F3,surf1, s = 0 .. 2*Pi, t = 0 .. Pi/2,
arrowcolour=blue, scalefactor = 1/4, arrowgrid=[10,5], arrowthickness=1, scaling=constrained, style=patchnogrid, orientation=[0,60]);
2 2 2
F3 := (x, y, z) -> [3 x z, 3 y z, 2 z - x - y ]
See also: arrow3d , curvarrows , plot3d
Maple Advisor Database
R. Israel, 1998