Our research activities broadly pertain to the numerical simulation of complex fluid flows with heat and mass transfer, mostly laminar or inertial (weakly turbulent at most). The approach is purely computational. Our contributions span the whole workflow, from the design of new numerical schemes, their parallel implementation (mostly in C/C++ and MPI) in our own in-house codes, the use of our codes on supercomputers to generate large data set to eventually the analysis of these data set with both traditional and Machine Learning techniques to design Physics-Informed data-driven mesoscale and macroscale models.
Applications range from industrial processes in the energy industry (fluidized beds, solid particle solar receivers, slurry transport), geophysical and environmental flows (sediment transport in rivers, landslides) to flows of biological fluids. The three main components of our research are:
Multiphase Flows
And primarily particle-laden flows. My group develops and integrates its own simulation tools in a multi-scale approach.
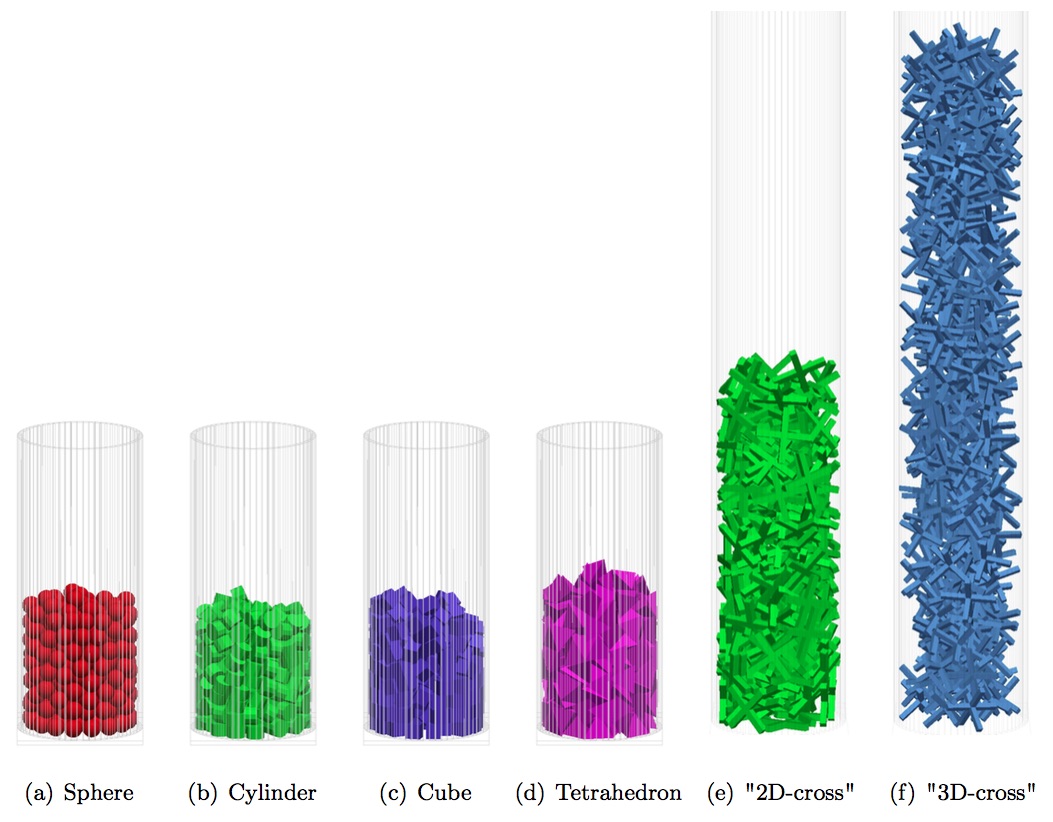 Packing particles on various shapes, including non-spherical, angular and non-convex shapes, in a small cylindrical reactor
Packing particles on various shapes, including non-spherical, angular and non-convex shapes, in a small cylindrical reactor
 A deformable capsule flowing through a 2:1 contraction (left) and a 4:1 contraction (right). Simulations are fully 3D and use dynamic octree adaptivity
A deformable capsule flowing through a 2:1 contraction (left) and a 4:1 contraction (right). Simulations are fully 3D and use dynamic octree adaptivity
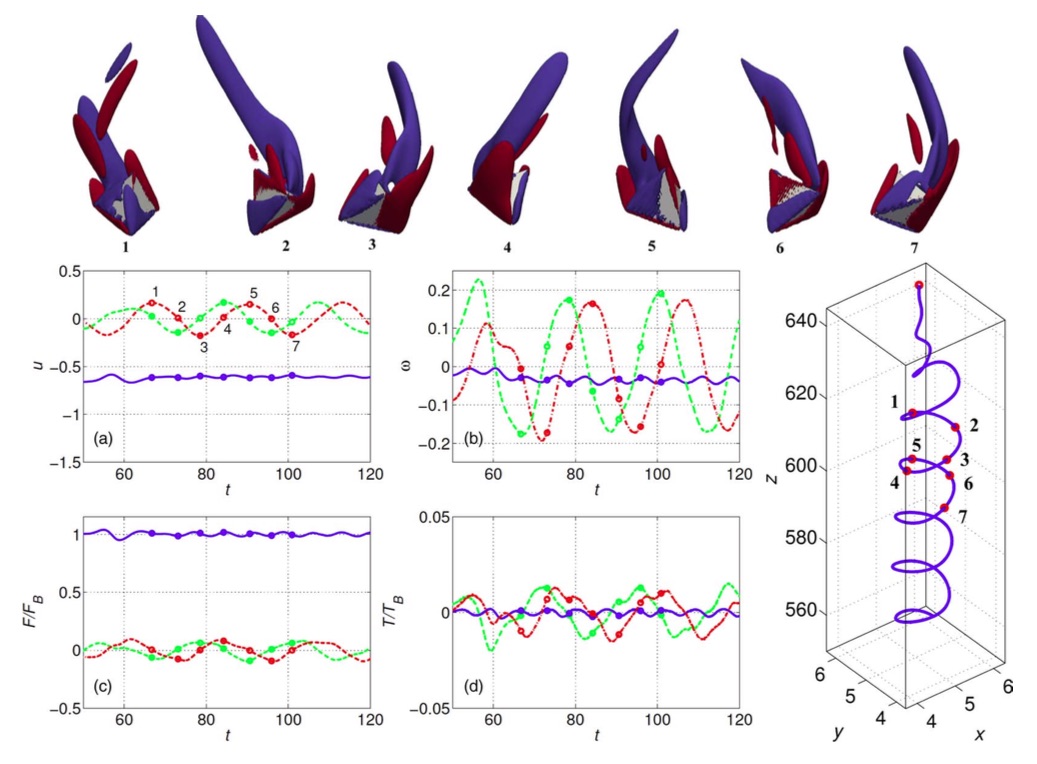 Spiralling motion of a regular tetrahedron settling in a Newtonian fluid at Re=139
Spiralling motion of a regular tetrahedron settling in a Newtonian fluid at Re=139
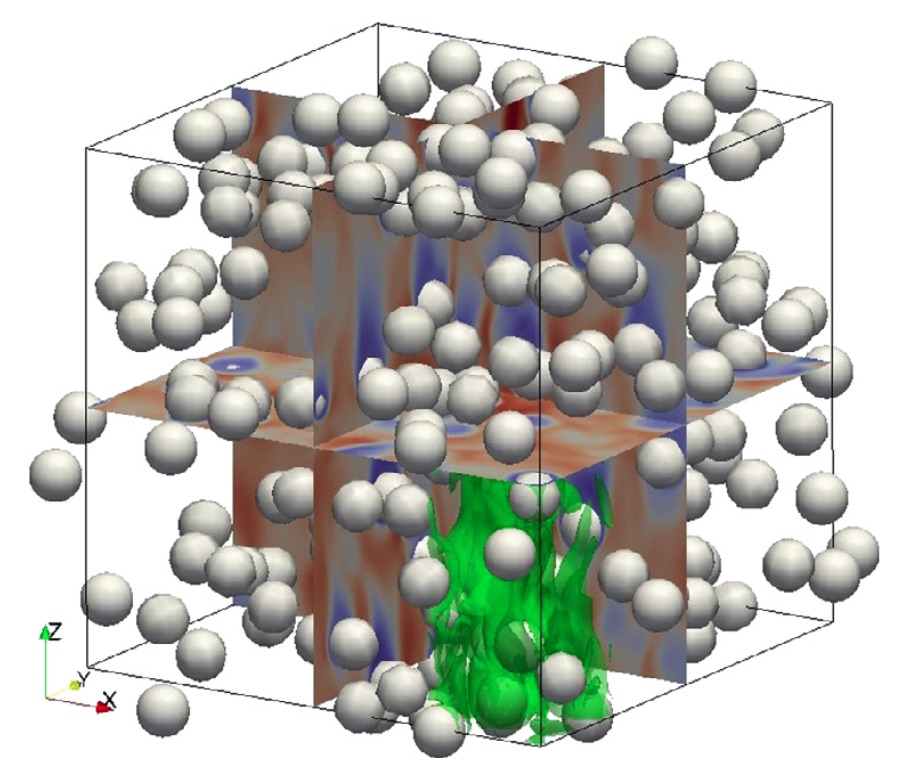 190 spheres settling in a tri-periodic box at Re=148 and φ=0.1
190 spheres settling in a tri-periodic box at Re=148 and φ=0.1
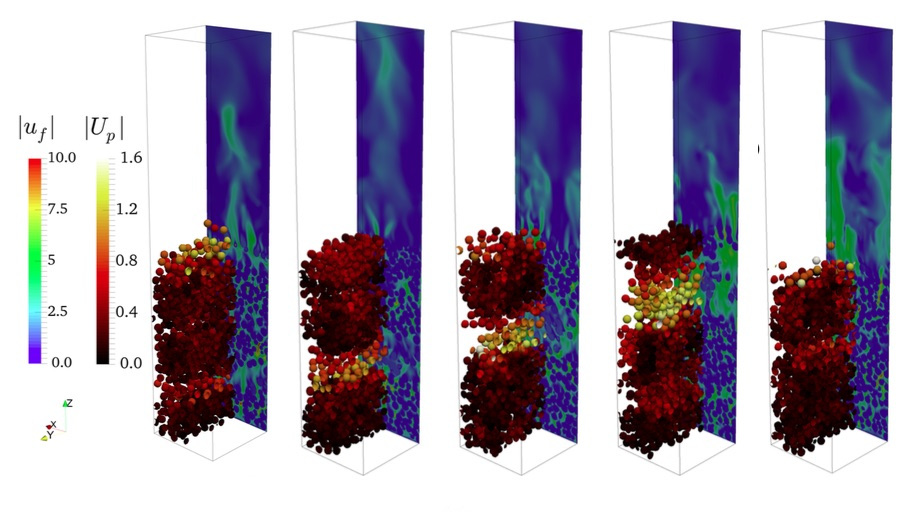 Gad/solid fluidization of 2,000 spheres at 2 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 85, Re is 29 and Fr is 0.49
Gad/solid fluidization of 2,000 spheres at 2 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 85, Re is 29 and Fr is 0.49
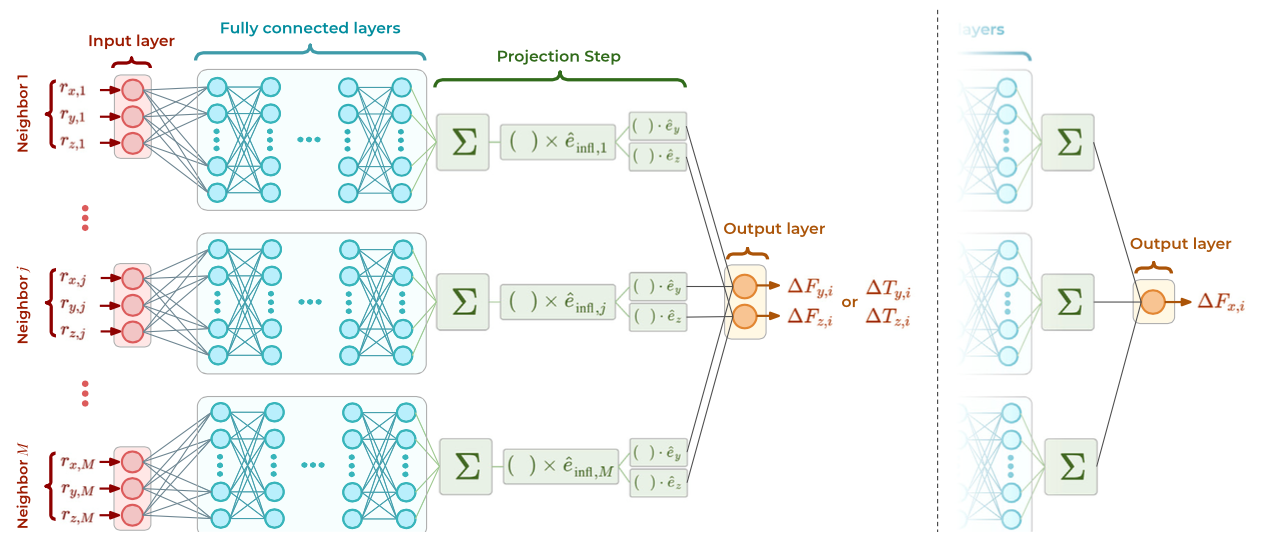 A Physics-Informed Neural Network model to predict the hydrodynamic force and torque exerted on individual spheres by the flow through a random array of stationary spheres
A Physics-Informed Neural Network model to predict the hydrodynamic force and torque exerted on individual spheres by the flow through a random array of stationary spheres
Publications
- A. Goyal, J.L. Pierson and A. Wachs. Hydrodynamic force interaction of two fixed spheres in a wall-bounded linear shear flow, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 172, 104720, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2024.104720
- A. Goyal, G. Gai, Z. Cheng, J.P. Cunha, L. Zhu and A. Wachs. Flow past a random array of statistically homogeneously distributed stationary Platonic polyhedrons: Data analysis, Probability maps and Deep Learning models, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 177, 104854, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2024.104854
- D. Huet, A. Morente, G. Gai and A. Wachs. Motion and deformation of capsules flowing through a corner in the inertial and non-inertial regimes, Physical Review Fluids, 9, 053601, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.9.053601
- G. Gai and A. Wachs. On the dynamics and wakes of a freely settling Platonic polyhedron in a quiescent Newtonian fluid, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 985, A3, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2024.269
- A. Goyal and A. Wachs. An accurate and scalable direction-splitting solver for flows laden with non-spherical rigid bodies - Part 2: Moving rigid bodies, Computers & Fluids, 271, 106178, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2024.106178
- A. Goyal and A. Wachs. An accurate and scalable direction-splitting solver for flows laden with non-spherical rigid bodies - Part 1: fixed rigid bodies, Communications in Computational Physics, 34, 1079-1132, 2023. https://doi.org/10.4208/cicp.OA-2023-0176
- Z. Cheng and A. Wachs. Physics-informed neural network for modelling force and torque fluctuations in a random array of bidisperse spheres, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 169, 104603, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2023.104603
- Z. Cheng and A. Wachs. Hydrodynamic force and torque fluctuations in a random array of polydis-
perse stationary spheres, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 167, 104524, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2023.104524
- G. Gai and A. Wachs. Dynamics, wakes and regime transitions of a fixed angular particle in an unbounded inertial flow - Part 1: regular tetrahedron angular position, Physical Review Fluids, 8,
064304, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.8.064304
- G. Gai and A. Wachs. Dynamics, wakes and regime transitions of a fixed angular particle in an unbounded inertial flow - Part 2: from tetrahedron to sphere, Physical Review Fluids, 8, 064305, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.8.064305
- G. Gai and A. Wachs. On the streamwise vorticity generation and distribution in an angular particle wake, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 964, R3, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2023.408
- L. Zhu and A. Wachs. Interpolation of probability-driven model to predict hydrodynamic forces and torques in particle-laden flows, AIChE Journal, 69(11), e18209, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.18209
- A.R. Ghigo, S. Popinet and A. Wachs. A conservative finite volume cut-cell method on an adaptive Cartesian tree grid for moving rigid bodies in incompressible flows, 2023.
https://hal.science/hal-03948786
- D.P. Huet and A. Wachs. A Cartesian-octree adaptive front-tracking solver for immersed biological capsules in large complex domains, Journal of Computational Physics, 492, 112424, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2023.112424
- Book chapter. A. Wachs, M. Ulhmann, J. Derksen and D.P. Huet. Modeling of short-range interactions between both spherical and non-spherical rigid particles, in Modeling Approaches and Computational Methods for Particle-Laden Turbulent Flows, Elsevier, Chap 7, 217-264, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-32-390133-8.00019-0
- Book chapter. A. Chouippe, A.G. Kidanemariam, J. Derksen, A. Wachs and M. Ulhmann. Results from particle-resolved simulations, in Modeling Approaches and Computational Methods for Particle-Laden Turbulent Flows, Elsevier, Chap 6, 185-216, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-32-390133-8.00014-1
- Book chapter. M. Ulhmann, J. Derksen, A. Wachs, L.-P. Wang and M. Moriche. Efficient methods for particle-resolved direct numerical simulation, in Modeling Approaches and Computational Methods for Particle-Laden Turbulent Flows, Elsevier, Chap 5, 147-184, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-32-390133-8.00013-X
- G. Gai and A. Wachs. High fidelity adaptive Cartesian octree grid computations of the flow past a Platonic polyhedron up to a Reynolds number of 200, Powder Technology, 420, 118390, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2023.118390
- G. Gai, Thomine, O., Hadjadj, A., Kudriakov, S. and A. Wachs. Preferential Concentration of Particles in Forced Turbulent Flows: Effects of Gravity, Energies, 16(6), 2910, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16062910
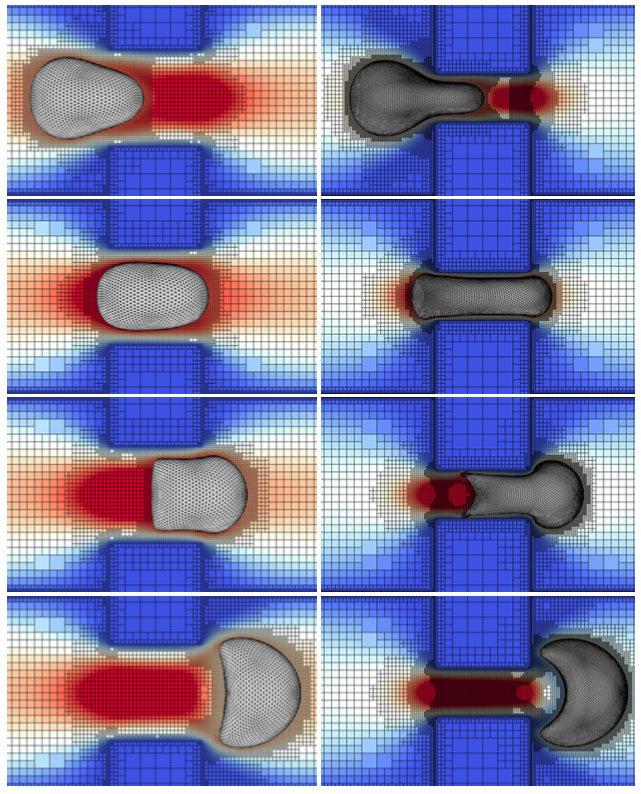
- L. Jbara, A.R. Ghigo and A. Wachs. Steady three-dimensional unbounded flow past an obstacle continuously deviating from a sphere to a cube, Physics of Fluids, 35, 013343, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0133499
- A. Seyed-Ahmadi and A. Wachs. Physics-inspired architecture for neural network modeling of forces and torques in particle-laden flows, Computers & Fluids, 238, 105379, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2022.105379
- Z. Cheng and A. Wachs. An Immersed Boundary/multi-relaxation time lattice Boltzmann method on adaptive octree grids for the particle-resolved simulation of particle-laden flows, Journal of Computational Physics, 471, 111669, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2022.111669
- C. Beaulieu, D. Vidal, C. Mitonkuru, A. Wachs, J. Chaouki and F. Bertrand. Effect of particle angularity on flow regime transitions and segregation of bidisperse blends in a rotating drum, Computational Particle Mechanics, 9, 443-463, 2022. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40571-021-00421-1
- F. Euzenat, A. Hammouti, E. Climent, P. Fede and A. Wachs. Effect of spatial filter features on local heat transfer coefficients obtained from particle-resolved simulations of a flow through a fixed random array of rigid spherical particles, International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 92, 108873, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2021.108873
- D. Huet, M. Jalaal, R. van Beek, D. van der Meer and A. Wachs. Granular avalanches of entangled rigid particles, Physical Review Fluids, 6, 104304, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.6.104304
- C. Selcuk, A.R. Ghigo, S. Popinet and A. Wachs. A fictitious domain method with distributed Lagrange multipliers on adaptive quad/octrees for the direct numerical simulation of particle-laden flows, Journal of Computational Physics, 430, 109954, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2020.109954
- A. Seyed-Ahmadi and A. Wachs. Sedimentation of inertial monodisperse suspensions of cubes and spheres, Physical Review Fluids, 6, 044306, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.6.044306
- A. Seyed-Ahmadi and A. Wachs. Microstructure-informed probabilistic point-particle model for hydrodynamic forces and torques in particle-laden flows, Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 900, A21-1-38, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2020.453
- M. Sulaiman, E. Climent, A. Wachs and A. Hammouti. Numerical simulations and modelling of mass transfer through random assemblies of catalyst particles: From dilute to dense reactive particulate regime, Chemical Engineering Science, 223, 115659, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.115659
- A. Seyed-Ahmadi and A. Wachs. Dynamics and wakes of freely settling and rising cubes. Physical Review Fluids, 4, 074304, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.074304
- J.L. Pierson, A. Hammouti, F. Auguste and A. Wachs. Inertial flow past a finite-length axisymmetric cylinder of aspect ratio 3: Effect of the yaw angle. Physical Review Fluids, 4, 044802, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevFluids.4.044802
- A. Wachs. Particle-scale computational approaches to model dry and saturated granular flows of non-Brownian, non-cohesive and non-spherical rigid bodies, Acta Mechanica, 230, 1919-1980, 2019. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00707-019-02389-9
- M. Sulaiman, A. Hammouti, E. Climent and A. Wachs. Coupling the fictitious domain and sharp interface methods for the simulation of convective mass transfer around reactive particles: Towards a reactive Sherwood number correlation for dilute systems. Chemical Engineering Science, 198, 334-351, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2019.01.004
- M. Sulaiman, E. Climent, A. Hammouti and A. Wachs. Mass transfer towards a reactive particle in a fluid flow : numerical simulations and modeling. Chemical Engineering Science, 199, 496-507, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2018.12.051
- M. Rolland, A.D. Rakotonirina, A. Devouassoux, J. Barrios Goicetty, J.Y. Delenne and A. Wachs. Predicting average void fraction and void fraction uncertainty in fixed beds of poly-lobed particles. Industrial & Engineering C hemistry Research, 58, 3902-3 911, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05557
- M. Rahmani, A. Hammouti and A. Wachs. Momentum balance and stresses in a suspension of spherical particles in a plane Couette flow. Physics of Fluids, 30, 043301, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5010989
- A.D. Rakotonirina, J.-Y. Delenne, F. Radjai, A. Wachs. Grains3D, a flexible DEM approach for particles of arbitrary convex shape - Part III: extension to non-convex particles modelled as glued convex particles. Computational Particle Mechanics, 6, 55-84, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40571-018-0198-3
- A. Esteghamatian, F. Euzenat, M. Lance, A. Hammouti and A. Wachs. A stochastic formulation for the drag force based on multiscale numerical simulation of fluidized beds. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 99:363-382, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2017.11.003
- A. Esteghamatian, M. Lance, A. Hammouti and A. Wachs. Particle resolved simulations of liquid/solid and gas/solid fluidized beds. Physics of Fluids, 29, 033302, 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4979137
- A. Esteghamatian, M. Bernard, M. Lance, A. Hammouti and A. Wachs. Micro/meso simulation of a fluidized bed in a homogeneous bubbling regime, International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 92:93-111, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2017.03.002
- M. Bernard, E. Climent and A. Wachs. Controlling the Quality of Two-Way Euler/ Lagrange Numerical Modeling of Bubbling and Spouted Fluidized Beds Dynamics. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 56(1):368-386, 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b03627
- A. Wachs, A. Hammouti, G. Vinay and M. Rahmani. Accuracy of Finite Volume/Staggered Grid Distributed Lagrange Multiplier/Fictitious Domain simulations of particulate flows. Computers & Fluids, 115:154-172, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2015.04.006
- F. Dorai, C. Moura Teixeira, M. Rolland, E. Climent, M. Marcoux and A. Wachs. Fully-resolved simulations of the flow through a packed bed of cylinders : effects of size distribution. Chemical Engineering Science, 129:180-192, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2015.01.070
- M. Rahmani and A. Wachs. Free falling and rising of spherical and angular particles. Physics of Fluids, 26:083301, 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4892840
- L. Girolami, A. Wachs and G. Vinay. Unchannelized dam-break flows : Effects of the lateral spread- ing on the flow dynamics. Physics of Fluids, 25:043306, 2013. http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4799129
- L. Girolami, V. Hergault, G. Vinay and A. Wachs. A three-dimensional discrete-grain model for the simulation of dam-break rectangular collapses : comparison between numerical results and experi- ments. Granular Matter, 14(3):381-392, 2012. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10035-012-0342-3?LI=true#
- A. Wachs, L. Girolami, G. Vinay and G. Ferrer. Grains3D, a flexible DEM approach for particles of arbitrary convex shape - Part I : numerical model and validations. Powder Technology, 224:374-389, 2012. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2012.03.023
- V. Topin, F. Dubois, Y. Monerie, F. Perales and A. Wachs. Micro-rheology of dense particulate flows : application to immersed avalanches. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 166(1):63-72, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2010.10.006
- A. Wachs. Rising of 3D catalyst particles in a natural convection dominated flow by a parallel DNS method. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 35(11):2169-2185, 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compchemeng.2011.02.013
- C. Dan and A. Wachs. Direct numerical simulation of particulate flow with heat transfer. Interna- tional Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 31:1050-1057, 2010. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2010.07.007
- A. Wachs. A DEM-DLM/FD method for direct numerical simulation of particulate flows : Sedimentation of polygonal isometric particles in a Newtonian fluid with collisions. Computers & Fluids, 38(8):1608-1628, 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2009.01.005
- Z. Yu, X. Shao and A. Wachs. A fictitious domain method for particulate flows with heat transfer. Journal of Computational Physics, 217(2):424-452, 2006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2006.01.016
- Z. Yu, X. Shao and A. Wachs. A fictitious domain method for particulate flows. Journal of Hydrodynamics, Ser. B, 18(3):482-486, 2006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1001-6058(06)60098-X
- Z. Yu, A. Wachs and Y. Peysson. Numerical simulation of particle sedimentation in shear-thinning fluids with a fictitious domain method. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 136(2-3):126- 139, 2006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2006.03.015
High Performance Computing
Most of our simulations are extremely resource-intensive. Our simulation tools are fully parallel and run on large supercomputers. Improving the scalability of my codes and designing faster algorithms is a strong component of our work.
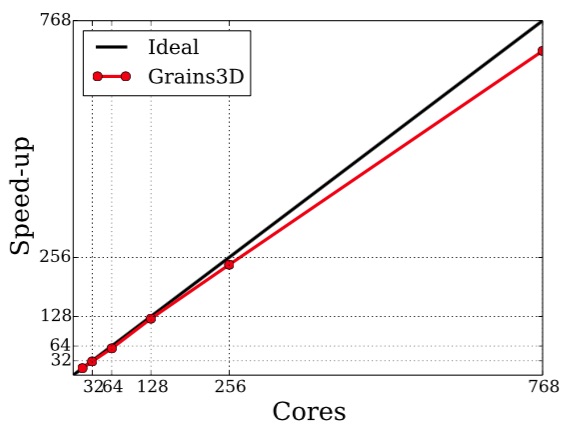 Large scale computing with a meso scale DEM-CFD model of a gas/solid fluidized bed with 19,200,000 spheres at 3 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 2083, Re is 79 and Fr is 0.007. Weak scalability of the DEM granular solver from 16 cores/4,800,000 particles to 768 cores/230,400,000 particles.
Large scale computing with a meso scale DEM-CFD model of a gas/solid fluidized bed with 19,200,000 spheres at 3 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 2083, Re is 79 and Fr is 0.007. Weak scalability of the DEM granular solver from 16 cores/4,800,000 particles to 768 cores/230,400,000 particles.
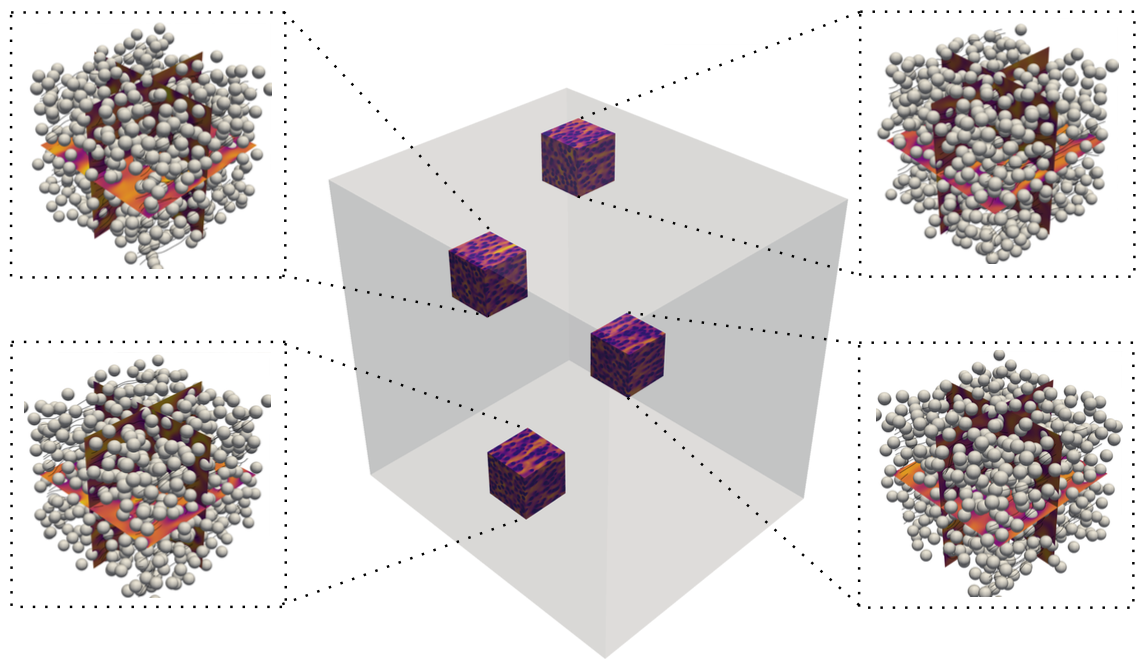 Flow past a random array of 144,327 stationary spheres at Re=19.2 and φ=0.15. Particle-Resolved computation with a spatial resolution of 24 cells per sphere diameter ran on 6,800 cores of the UBC Sockeye supercomputer and 6,800,000,000 cells.
Flow past a random array of 144,327 stationary spheres at Re=19.2 and φ=0.15. Particle-Resolved computation with a spatial resolution of 24 cells per sphere diameter ran on 6,800 cores of the UBC Sockeye supercomputer and 6,800,000,000 cells.
Publications
- A. Morente, A. Goyal and A. Wachs. A Highly Scalable Direction-Splitting Solver on Regular Cartesian Grid to Compute Flows in Complex Geometries Described by STL Files, Fluids, 8(3), 86, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids8030086
- A.D. Rakotonirina and A. Wachs. Grains3D, a flexible DEM approach for particles of arbitrary convex shape - Part II: parallel implementation and scalable performances. Powder Technology, 324, 18-35, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2017.10.033
- A. Wachs. PeliGRIFF, a parallel DEM-DLM/FD direct numerical simulation tool for 3D particulate flows. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 71(1):1-25, 2010. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10665-010-9436-2?LI=true#
Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics
The focus is on viscoplastic materials and the way they flow. My group develops and extends existing numerical methods to simulate yield stress fluid flows in assorted conditions (heat transfer, liquid/liquid interface, solid particles).
 |
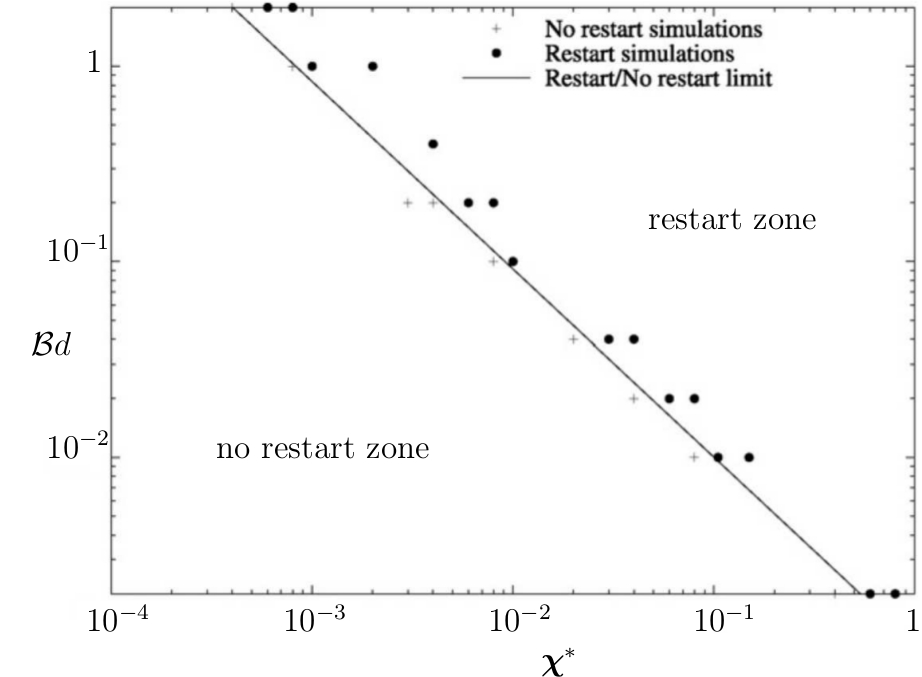
Restart flow map for Bn=0.55
|
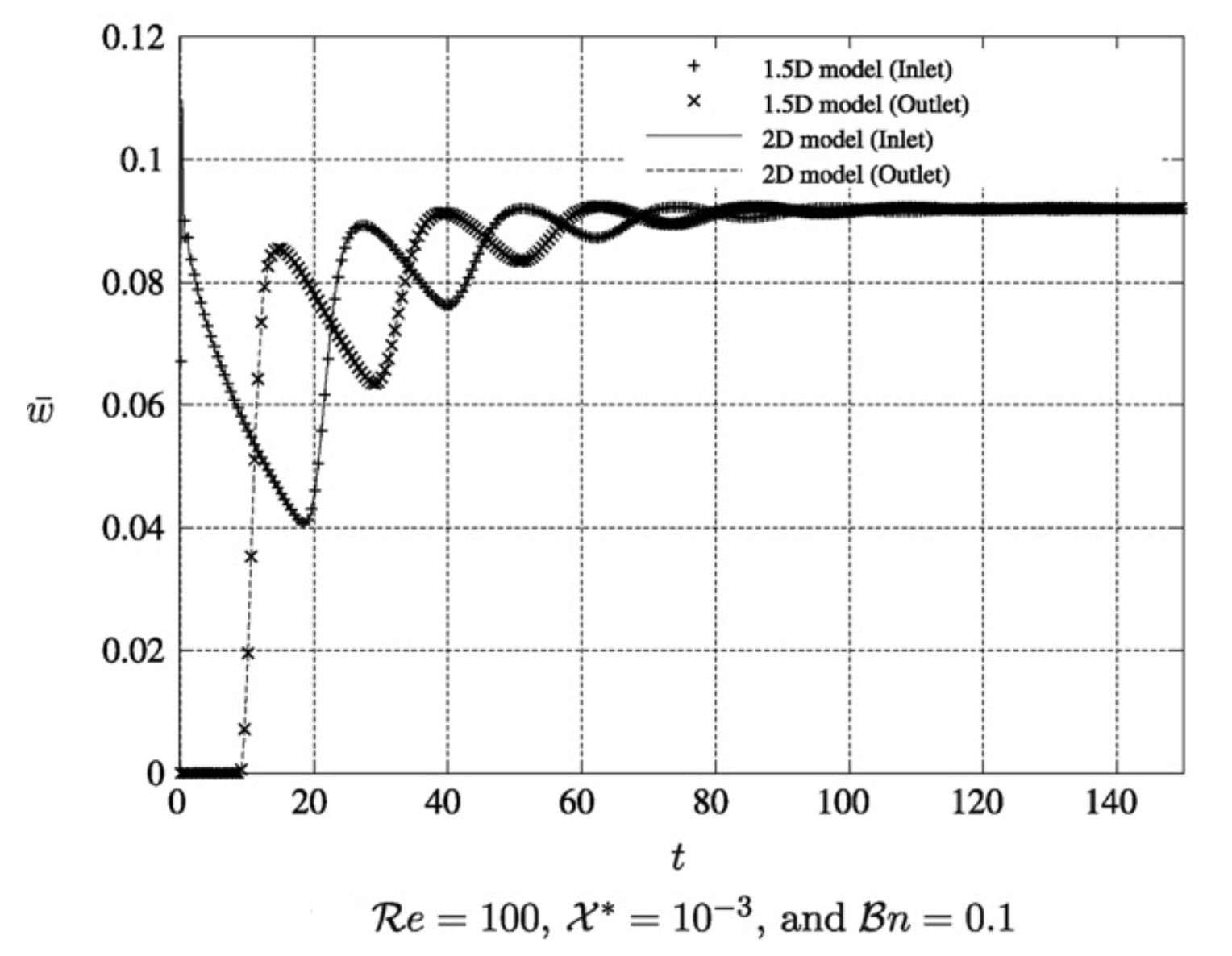
Restart of a weakly compressible flow of a viscoplastic and thixotropic fluid: application to the restart of a pipeline filled with a gelled waxy crude oil
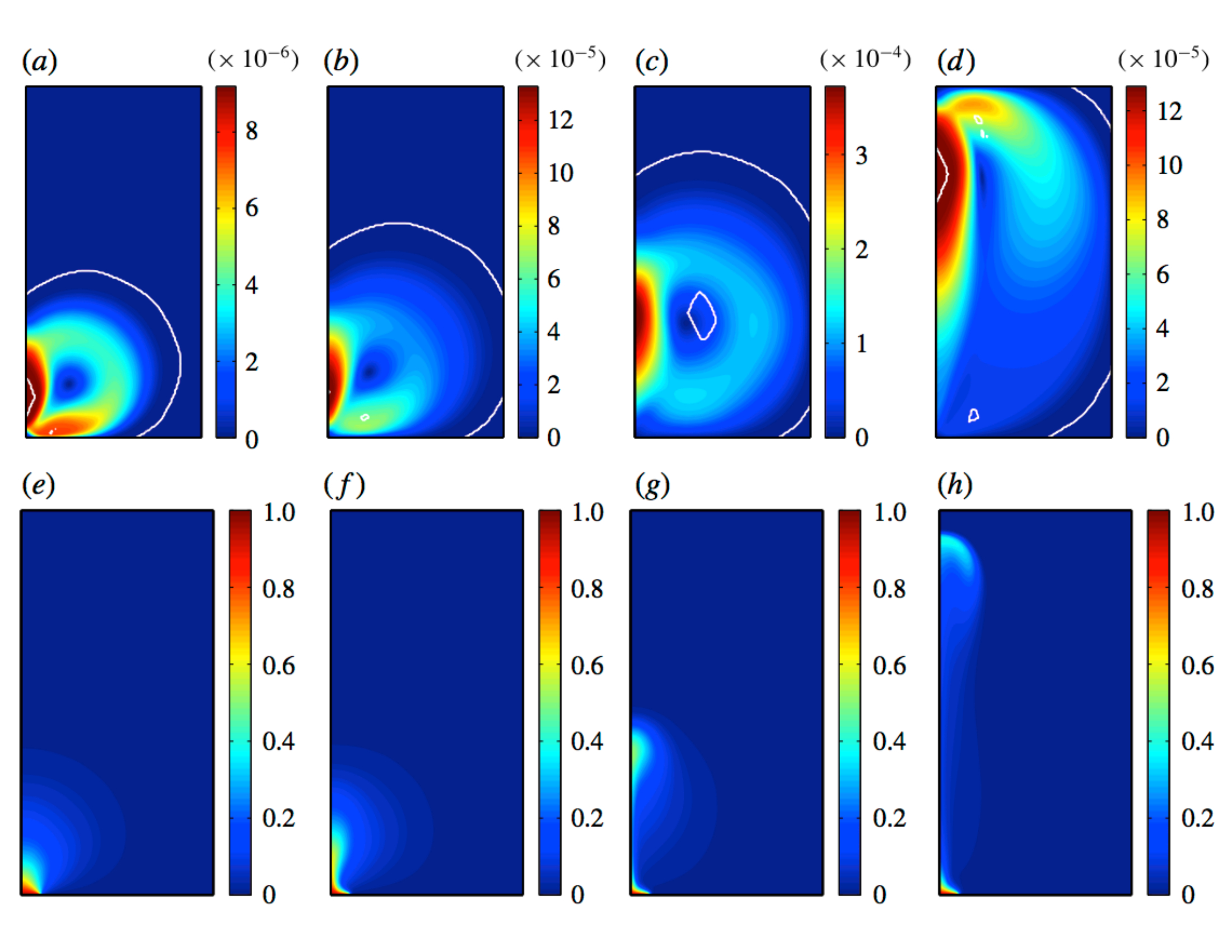 Thermal plumes in a viscoplastic fluid
Thermal plumes in a viscoplastic fluid
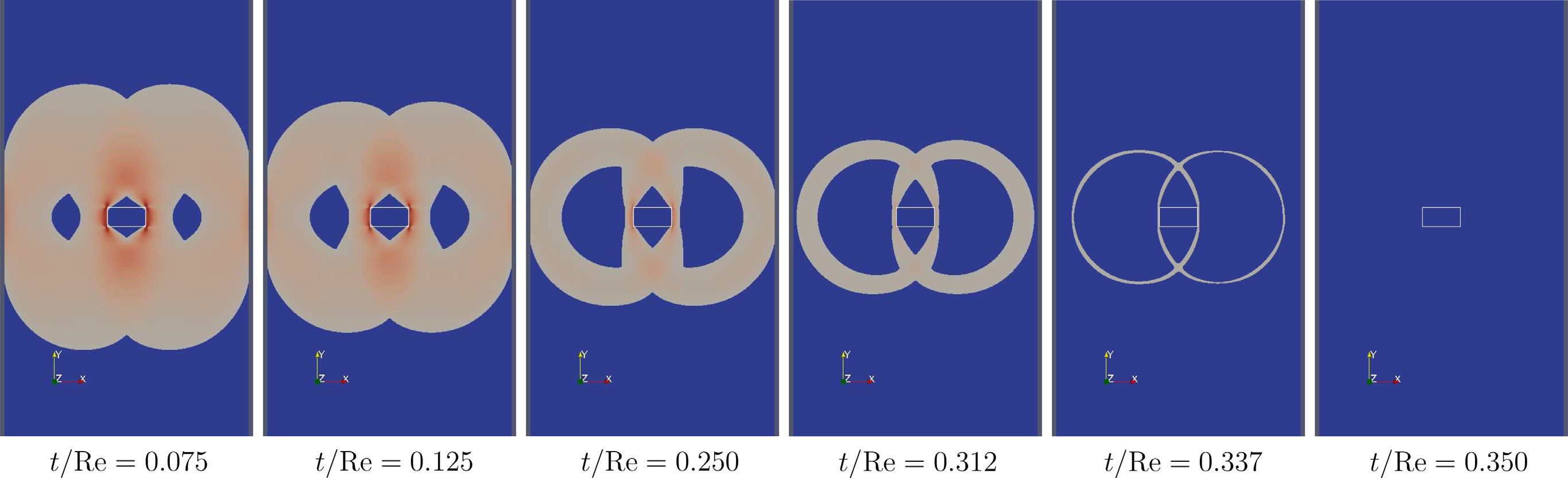 A solid rectangle settling in a viscoplastic fluid returning back to rest in a finite time as a result of an increase of the Bingham number beyond the critical stability limit
A solid rectangle settling in a viscoplastic fluid returning back to rest in a finite time as a result of an increase of the Bingham number beyond the critical stability limit
Publications
- J. MacKenzie, E. Siren, M. Daneshi, R. Melnick, T. Treskatis, A. Wachs, J.N. Kizhakkedathu, D.M. Martinez. Fibre-reinforced biocompatible hydrogel to replace single-use plastic tubing in the clinical setting, Chemical Engineering Journal, 428, 131786, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131786
- T. Treskatis, A. Roustaei, I. Frigaard, A. Wachs. Practical guidelines for fast, efficient and robust simulations of yield-stress flows without regularisation: A study of accelerated proximal gradient and augmented Lagrangian methods. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 262:149-164, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2018.05.002
- E. Chaparian, A. Wachs and I. Frigaard. Inline motion and hydrodynamic interaction of 2D particles in a viscoplastic fluid. Physics of Fluids, 30, 033101, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5022109
- P. Saramito and A. Wachs. Progress in numerical simulation of yield stress fluid flows. Rheologica Acta, 56(3):211-230, 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00397-016-0985-9
- A. Wachs and I. Frigaard. Particle settling in yield stress fluids: Limiting time, distance and applications. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 238:189-204, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2016.09.002
- I. Karimfazli, I. Frigaard and A. Wachs. Thermal plumes in viscoplastic fluids: flow onset and development. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 787:474-507, 2016. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2015.639
- I. Karimfazli, I. Frigaard and A. Wachs. A novel heat transfer switch using the yield stress. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 783:526-566, 2015. http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2015.511
- Book chapter. R. Glowinski and A. Wachs. Numerical Methods for Non-Newtonian Fluids, Volume 16: Special Volume (Handbook of Numerical Analysis), volume XVI, chapter On the numerical simulation of viscoplastic fluid flow, pages 483-718. North-Holland, Amsterdam, 2011.
- A. Wachs, G. Vinay and I. Frigaard. A 1.5 D numerical model for the start up of weakly compressible flow of a viscoplastic and thixotropic fluid in pipelines. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 159(1-3):81-94, 2009. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2009.02.002
- Z. Yu and A. Wachs. A fictitious domain method for dynamic simulation of particle sedimentation in Bingham fluids. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 145(2- 3):78-91, 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.02.007
- I. Frigaard, G. Vinay and A. Wachs. Compressible displacement of waxy crude oils in long pipeline startup flows. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 147(1-2):45-64, 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.07.002
- G. Vinay, A. Wachs and I. Frigaard. Start-up transients and efficient computation of isothermal waxy crude oil flows. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 143(2-3):141-156, 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2007.02.008
- A. Wachs. Numerical simulation of steady Bingham flow through an eccentric annular cross-section by distributed Lagrange multiplier/fictitious domain and augmented Lagrangian methods. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 142(1-3):183-198, 2007. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2006.08.009
- G. Vinay, A. Wachs and J.F. Agassant. Numerical simulation of weakly compressible Bingham flows : The restart of pipeline flows of waxy crude oils. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 136(2-3):93-105, 2006. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2006.03.003
- G. Vinay, A. Wachs and J.F. Agassant. Numerical simulation of non-isothermal viscoplastic waxy crude oil flows. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 128(2-3):144-162, 2005. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jnnfm.2005.04.005
- A. Wachs, J.R. Clermont, and A. Khalifeh. Computations of non-isothermal viscous and viscoelastic flows in abrupt contractions using a finite volume method. Engineering Computations, 19(8):874-901, 2002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/02644400210450332
- A. Wachs and J.R. Clermont. Non-isothermal viscoelastic flow computations in an axisymmetric contraction at high Weissenberg numbers by a finite volume method. Journal of Non-Newtonian Fluid Mechanics, 95(2-3):147-184, 2000. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0257(00)00176-2
- A. Wachs, J.R. Clermont and M. Normandin. Fully-developed flow and temperature calculations for rheologically complex materials using a mapped circular domain. Engineering Computations, 16:807-830, 1999. http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/02644409910298138
|




 Gad/solid fluidization of 2,000 spheres at 2 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 85, Re is 29 and Fr is 0.49
Gad/solid fluidization of 2,000 spheres at 2 times the minimal fluidization velocity. Solid/gas density ratio is 85, Re is 29 and Fr is 0.49
 A Physics-Informed Neural Network model to predict the hydrodynamic force and torque exerted on individual spheres by the flow through a random array of stationary spheres
A Physics-Informed Neural Network model to predict the hydrodynamic force and torque exerted on individual spheres by the flow through a random array of stationary spheres









