| Malin's Magnificent Math |
|
Home
Colour: Physics & Light Reflection Functions Illumination Models Ray Tracing |
RadiometryWhat is radiometry?Radiometry is the science of light (electromagnetic) energy measurement.Calculating angles and solid angles: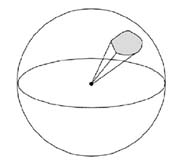
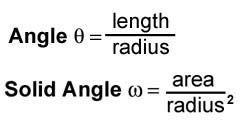 The circle has 2π radians. The sphere has 4π steradians. Differential Solid Angles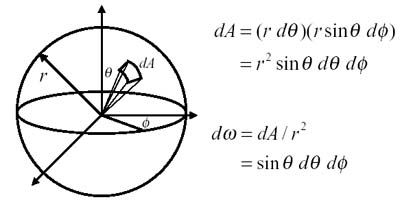 Projected Solid Angle: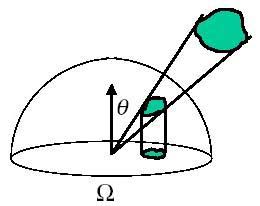
 Projection of the differential area (on the sphere's surface) onto the base of the sphere. 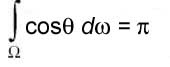 What is radiance?Radiance (or luminance) is the power per unit area per unit solid angle.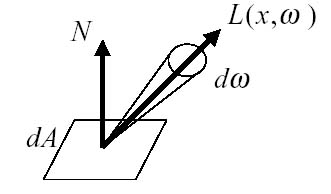 Symbol: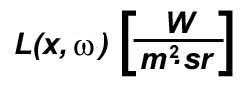 Flux: Radiant PowerRadiant Properties:
What is Irradiance?Irradiance (illuminace) is the power per unit area incident on a surface.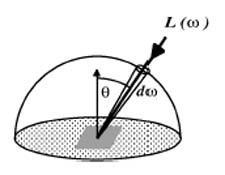 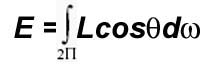
What is Radiosity?Radiosity (luminosity) is the power per unit area leaving a surface.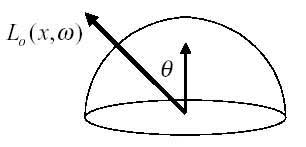 What is Radiant Intensity?Radiant intensity is the radiant power per solid angle of a point source.
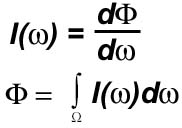 Irradiance: Distance Source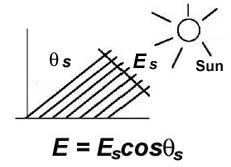
Irradiance: Point Source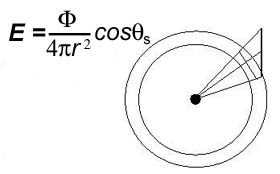 |